5 Risks Of Web 3.0
5 Risks Of Web 3.0
The early days of the internet had only static web pages developed by people, companies and government for serving information like important announcements. Subsequently, the world came to know social media platforms and new ways for users to contribute content to the web. However, the benefits of user-generated content did not overshadow the manipulation of user data for personal gains by centralized institutions. While web3 has the potential to resolve existing setbacks with the web, it is also important to identify web 3.0 risks and their impact on the broader web.
Web3 has the right components and implications for ensuring easier access to information and services without compromising the integrity of user data and personal information. On the other hand, concerns regarding the security risks with web3 would also take the limelight in defining the future of web3. The following discussion dives deeper into an outline of prominent security risks for web3 ecosystem.
The early days of the internet had only static web pages developed by companies for serving information like important announcements. Subsequently, the world came to know social media platforms and new ways for users to contribute content to the web. However, the benefits of user-generated content did not overshadow the manipulation of user data for personal gains by centralized institutions. While web3 has the potential to resolve existing setbacks with the web, it is also important to identify web 3.0 risks and their impact on the broader web.
Web3 has the right components and implications for ensuring easier access to information and services without compromising the integrity of user data and personal information. On the other hand, concerns regarding the security risks with web3 would also take the limelight in defining the future of web3. The following discussion dives deeper into an outline of prominent security risks for web3 ecosystem.
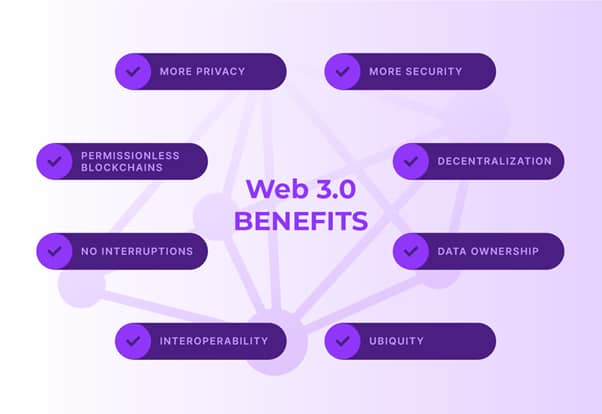
Why Does the Web 3.0 Matter?

The discussion on web3 security must emphasize its significance. Why is web3 so important that you have to worry about risks in web3? According to the classic definitions of web3, the concept of ‘semantic web3’ provides an almost realistic explanation for how web3 would work. Semantic web basically implies that all the data on the web would be machine-readable.
The semantic metadata of a webpage provides a detailed meaning of different elements of the webpage to computers. The internet works as a massive and connected database on the basis of semantic metadata. Search queries rely on capabilities of machines for reading the semantic metadata to facilitate contextually appropriate search results with better accuracy.
The importance of web3 could shed further light on the necessity for identifying web3 security risks and their impact. In the case of web2, search engines would offer results on the basis of keywords in web content. As a result, there is no way web2 search engines would consider contextual understanding. On the contrary, web3 can help in better information analytics and transactions through a deeper contextual understanding of all pages.
Apart from the “semantic web” traits, web3 also emphasizes it distributed networking or decentralization to resolve pressing concerns with web2. Decentralization helps in preventing the unwarranted influence of big tech companies such as Google, Facebook and Twitter on access to internet services. Users have the freedom to interact with sites and apps without any permission. At the same time, web3 also allows complete control over its own data to users without any centralized intermediaries.
Let’s take a look at five bottlenecks in next-generation Internet cyber security.
Issue 1. Data security
Since Web 3.0 is built on blockchain, cyber security experts have to come up with a mechanism to close loopholes for hackers and block data leakage. If attackers manage to steal a digital asset, it will be almost impossible to get it back. Indeed, in a decentralized network, it is difficult to track transaction paths.
Even though blockchain is considered one of the most secure technologies (records added to blocks are securely encrypted), it also has its issues. 51% attacks, Sybil attacks, phishing attacks, and theft of a user’s key — hackers have found vulnerabilities in such a seemingly solid system.
Wallet cloning is a common Web 3.0 security issue. If a hacker manages to get a user’s passphrase, they can make a copy of the wallet and use it to pay for services.
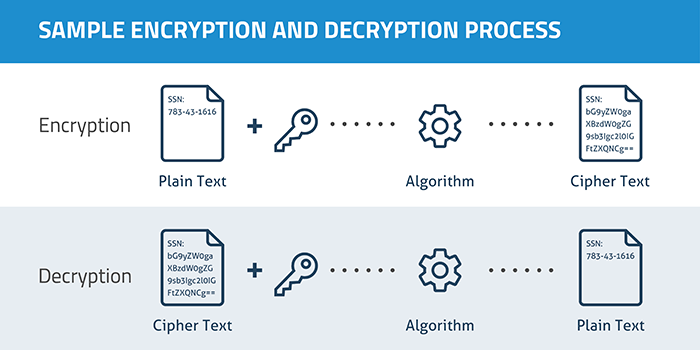
Issue 2.User authentication and signature
Most dApps do not authenticate or sign responses to requests. That is, when a user’s digital wallet receives data from such apps, it is impossible to verify that the response is sent by a real app and that the data is not fake. Therefore, developers in web 3.0 should initially consider how to ensure basic user security. They must develop effective mechanisms for finding and preventing risks.
Issue 3. Reliability of information
Since everything is decentralized in Web 3.0, experts have doubts about the authenticity and originality of information. The following questions remain unanswered: “How will the mechanism for checking security and accuracy work?”, “Who will confirm the validity of data?”, “How to calculate and prevent data manipulation?”. These issues still cause controversy. The sooner a solution to these problems is found, the sooner we will come to Web 3.0.
Issue 4. Data availability
The over-dependence of users on data in Web 3.0 is also puzzling. It is difficult to predict how the built systems will behave and what will happen to the processes if the data in them suddenly becomes unavailable. Experts argue what will happen to the whole network if one or two nodes fall out.
Issue 5. It will require large-scale reform
The tech community is actively discussing Web 3.0, the new version of the Internet. Although the concept of a modernized network is more or less clear, there is still no lucid algorithm for a large-scale reform of the digital environment. Cornell University professor James Grimmelmann says Web 3.0 will fix everything people don’t like about web 2.0, even if it’s controversial. And while the evolution of the Internet has great prospects, it does not rule out serious Web 3.0 security issues.
Conclusion: rethinking security in the age of the Metaverse
Web 3.0 challenges old models of networking. The new Internet of blockchains addresses the vital issues of its predecessor related to privacy and the risk of data loss. However, it does not exclude the emergence of new security holes related to smart contract hacks or the lack of legal documents to protect users of a blockchain network.
The distributed nature of the Internet may make it more difficult to detect and prevent cybercrime, misinformation, or spam. It is difficult to imagine how to regulate the activity of a blockchain-based site in different parts of the world, with different laws.
Regulators, businesses, and web users need to understand how Web 3.0 will protect their privacy to embrace the coming changes and seamlessly interact with others in the digital world.