Schema Markup
In the ever-evolving world of SEO, businesses are increasingly turning to a powerful tool called “schema” to enhance their web presence. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of schema, exploring its origins, diverse types, and the SEO implications of incorporating it into your website.
Understanding Schema: A Brief Overview
 What is Schema?
What is Schema?
Schema, also known as “structured data,” operates as a markup language that guides search engines in extracting additional information from webpages or entire websites. The schema vocabularies are collaboratively developed through the schema.org initiative, a unique collaboration among major search engines, including Google, Microsoft (Bing), Yahoo, and Yandex.
It may sound complex, but essentially you are telling search algorithms how best to interpret the content on your website, so it can be displayed in a more useful way. For example, Schema Markup can call attention to the difference between a product sales page listing for a microwave and a product review or that same microwave, or even a recipe that encourages the use of that microwave.
In each of those situations, the content will appeal to very different search intent, and schema markup can help search engines show the right content to the right searchers, potentially improving your website’s SEO.
Does Schema Help SEO

There are no guarantees that Schema Market will have a direct impact on your SEO, but by improving the relevance of your listings in search results as well as providing more enhanced details within the results, your click-through rate is likely to improve, which can have a significant, though indirect, effect on your SEO strategy.
The ultimate goal of Schema is to provide a better user experience when they’re using search engines, which is undeniably an important factor in ranking.
Who Created Schema?
Established in 2011, schema.org emerged from an unprecedented collaboration among major search engine players. Google, Microsoft (Bing), Yahoo, and Yandex collectively agreed on a standardized programming language, simplifying the process for webmasters who no longer needed to install separate markups for each search engine.
The Coding Languages of Schema
Schema utilizes three coding languages for creating markup:
- Microdata
- RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes)
- JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data)
Since 2017, Google recommends using JSON-LD, which is widely adopted for schema implementation.
Unveiling the Extra Tidbits: How Schema Works
Schema provides search engines with additional information beyond the standard webpage content. These snippets of code, implemented in various schema types, can include details like reviews, information about local businesses, events, and more. However, installing schema doesn’t guarantee that search engines will utilize the provided information; it depends on their algorithms.
 Diverse Types of Schema
Diverse Types of Schema
As of 12/2/2023 there are 803 Types, 1466 Properties 14 Datatypes, 87 Enumerations and 463 Enumeration members. https://schema.org/docs/schemas.html#:~:text=The%20schemas%20are%20a%20set,Enumerations%20and%20463%20Enumeration%20members.
Here’s an extensive list of 50 types of schema that businesses and organizations can consider for enhancing their online presence:
-
- Organization Schema: General information about businesses, nonprofits, or NGOs.

- Local Business Schema: Organization schema has hundreds of subsets of types of businesses. One of the most common subtypes of organization schema is local business schema. This schema type extracts information about a specific brick-and-mortar business location and can include things such as the address and phone number, price range, accepted payment options, hours of operation and more. This schema type is really valuable for local SEO and is one of our favorite schemas.
- Person Schema: Information about individuals, including job titles and social media profiles.

- Recipe Schema: Enhances visibility of online recipes in search engine results.

- Product Schema: Provides additional information about products, essential for e-commerce.

- Review Schema: Adds reviews to pages describing items, boosting click-through rates.

- Breadcrumb Schema: Displays path links on search engine results pages, aiding user navigation. Breadcrumb schema is a useful way to depict on the search engine results page the path links that lead to the page. It can help users determine from search results if a page is located where they would like to click within the website— this particular type of schema should help reduce the bounce rate on your site.
- Event Schema: Lists upcoming events on a website, including time, price, and location.
- Job Posting Schema: Allows businesses to list job openings, visible in search engine results.
- Video Schema: Provides metadata about videos, improving their visibility on search engines.
- Article Schema: Enhances the presentation of articles in search results with structured data.
- FAQ Schema: Presents Frequently Asked Questions in a structured format on search results.
- Course Schema: Provides details about educational courses offered on a website.
- Medical Schema: Includes health-related information, suitable for medical websites.
- Q&A Page Schema: Optimizes pages with question-and-answer content for search engines.
- Service Schema: Highlights services offered by businesses with additional details.
- Software Application Schema: Provides structured data for software applications.
- Travel Agency Schema: Offers details about travel agencies, useful for the travel industry.
- Hotel Schema: Enhances information about hotels, including ratings and reviews.
- Book Schema: Adds structured data for books, useful for authors and publishers.
- Music Album Schema: Provides metadata about music albums, aiding music-related sites.
- Restaurant Schema: Displays details about restaurants, including menus and reviews.
- Recipe Collection Schema: Organizes collections of recipes for better search visibility.
- WebPage Schema: General schema for web pages, improving overall search appearance.
- Place Schema: Highlights details about physical locations, relevant for various businesses.
- Recipe Ingredient Schema: Provides detailed information about ingredients used in recipes.
- Travel Itinerary Schema: Structured data for travel itineraries, useful for travel websites.
- Comic Story Schema: Adds structured data for comic stories or series.
- Broadcast Event Schema: Highlights details about broadcasted events, relevant for media.
- Government Organization Schema: Provides information about government organizations.
- Photograph Schema: Adds structured data for photographs, aiding photography websites.
- How-To Schema: Enhances how-to guides or tutorials with structured data.
- Mobile Application Schema: Provides metadata for mobile applications.
- Credit Card Schema: Offers details about credit cards and financial products.
- Critic Review Schema: Adds structured data for reviews from critics.
- Contact Page Schema: Optimizes contact pages for search engines.
- Payment Page Schema: Structured data for payment pages on e-commerce sites.
- User Review Schema: Presents user reviews in a structured format.
- Medical Clinic Schema: Provides information about medical clinics or health centers.
- Radio Episode Schema: Structured data for individual radio episodes.
- Special Announcement Schema: Highlights special announcements on websites.
- Animal Shelter Schema: Provides details about animal shelters and adoption centers.
- Motorcycle Schema: Adds structured data for motorcycles, relevant for dealerships.
- Product Model Schema: Provides details about specific product models.
- Social Media Profile Schema: Optimizes social media profiles for search engines.
- Course Instance Schema: Adds structured data for specific instances of educational courses.
- Dentist Schema: Provides information about dental practices and services.
- Payment Method Schema: Structured data for accepted payment methods.
- Plumber Schema: Highlights information about plumbing services and professionals.
- TV Series Schema: Adds structured data for television series and episodes.
- Organization Schema: General information about businesses, nonprofits, or NGOs.
Implementing Schema: Installation and Testing
How to Install Schema:
Google recommends using JSON-LD markup whenever possible. Webmasters can use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper to generate appropriate JSON-LD code, which is then inserted below the head section of the webpage. CMS platforms like WordPress offer plugins to simplify schema creation and installation.
How To Use Schema Markup Generators
There are a few different Schema Markup generators that you can use, but since Google is the undeniable giant in the world of search engines, we prefer to use their tool to ensure the best compatibility with their search engine. With just a few, well-guided steps, you can generate Schema Markup for your website in minutes.
- Navigate to Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
- Choose the Type of Data you want to incorporate into your website
- Enter the URL of your webpage that needs market
- Tag – the page will walk you through the process and give you all the options you need to customise your webpage with the correct data items
- Click the “Create the HTML” button when you’re satisfied with your work
- Download the HTML file with the automatically generated Schema Markup
- download the automatically-generated HTML file, and copy/paste it into your CMS or source code.
- Click the “Finish” button and a popup of “Next Steps” will guide you forward
Testing Schema
It is also always a good idea to test your Schema Markup. You can paste the HTML into your CMS or directly into the source code of your website and then use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to see what your page will look like in search results. You can also paste the generated HTML code directly into this tool before publishing it to your website to be sure you’re happy with the results. Correctly installed schema items will be recognized as valid, while errors or warnings may indicate issues with the code.
SEO Implications of Schema
While Google and Bing assert that schema is not a direct ranking factor, its indirect benefits contribute to enhanced web visibility. Listings with schema often appear prominently on search engine results pages, potentially leading to higher click-through rates, lower bounce rates, and an improved overall user experience.
Peeling Back the Layers: How Schema Adds Value
Schema enriches search engine results by providing additional information beyond typical webpage content. These coded snippets, embedded in diverse schema types, can encompass reviews, local business details, events, and more. However, it’s important to note that implementing schema doesn’t guarantee its immediate utilization by search engines, as this depends on their algorithms.
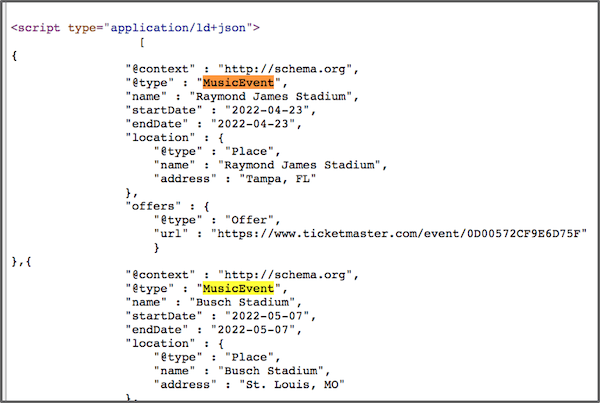
Here is what the Schema code looks on the backend.
In conclusion, integrating schema into your website stands as a strategic move for elevating your online presence. If you’re considering implementing schema and believe your website could benefit, our seasoned development and digital marketing teams at Webspec Design are ready to assist. Contact our sales team to explore how schema can become a catalyst for expanding your search engine presence, paving the way for digital success.