Building a Decentralized Social Community on Web3: A Comprehensive Guide
Building a Decentralized Social Community on Web3: A Comprehensive Guide
Concerns over data privacy and centralized control have prompted a growing interest in decentralized alternatives to traditional social media platforms. Web3 technology offers businesses the opportunity to create decentralized social communities that prioritize user ownership, privacy, and community governance. In this SEO-optimized article, we’ll explore the steps businesses can take to build their own decentralized social community on Web3, incorporating features such as DAOs and strategic roadmaps.
The Web3 market is anticipated to achieve a valuation of $107.32 billion by 2025.
Moreover, by 2026, approximately 2 billion individuals will dedicate at least one hour daily to the metaverse for work, shopping, education, socializing, or entertainment.
1. Understanding the Need for Decentralization
Centralized social media platforms have long been criticized for their exploitation of user data and lack of transparency in decision-making. Building a decentralized social community on Web3 addresses these concerns by putting control back into the hands of users. By leveraging blockchain technology and decentralized protocols, businesses can create a more equitable and user-centric social network.
2. Choosing the Right Blockchain Platform
The first step in building a decentralized social community is selecting the appropriate blockchain platform. Ethereum, with its robust ecosystem and support for smart contracts, is a popular choice for building decentralized applications (dApps). Other platforms such as Polkadot and Solana offer scalability and interoperability features that may be advantageous for certain use cases. Consider factors such as scalability, security, and developer support when choosing the right blockchain platform.
3. Developing the Protocol and Smart Contracts
Once the blockchain platform is selected, businesses can begin developing the protocol and smart contracts that will power the decentralized social community. This includes functionalities such as user authentication, content creation, curation, and interaction. Implement decentralized identity solutions to protect user privacy and ensure data sovereignty. Smart contracts can also facilitate community governance through DAOs, allowing users to participate in decision-making processes.
4. Implementing Community Governance through DAOs
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) play a crucial role in the governance of decentralized social communities. DAOs enable community members to propose, vote on, and implement changes to the platform, fostering transparency and inclusivity in decision-making. Implementing DAOs requires careful planning and consideration of governance mechanisms, voting mechanisms, and tokenomics. Establish a clear roadmap for DAO implementation and community participation.
5. Designing Tokenomics and Incentives
Tokenomics plays a central role in incentivizing user participation, content creation, and community engagement. Design a tokenomics model that rewards users for their contributions and aligns incentives between stakeholders. Introduce utility tokens or governance tokens that grant users voting rights and access to platform features. Implement mechanisms such as staking, voting, and rewards distribution to foster a vibrant and active community.
6. Roadmap and Launch Strategy
Develop a strategic roadmap outlining the key milestones and objectives for building and launching the decentralized social community. Define clear timelines, deliverables, and success metrics to track progress and measure success. Communicate the roadmap to the community to build excitement and gather feedback. Launch the decentralized social community in phases, starting with a minimum viable product (MVP) and iterating based on user feedback and community input.
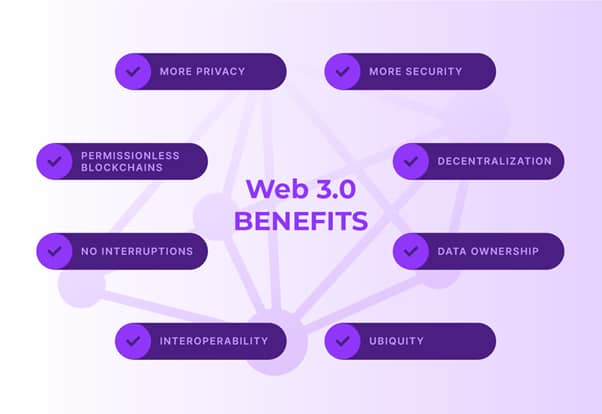
Pros of Web3:
- Decentralization: Web3 operates on decentralized networks, reducing reliance on centralized authorities and eliminating single points of failure. This enhances resilience, censorship resistance, and promotes greater user control over data.
- Data Ownership: In Web3, users have full ownership and control over their data, thanks to blockchain technology. This mitigates concerns over data privacy and reduces the risk of unauthorized access or exploitation by centralized entities.
- Trustless Transactions: Web3 enables trustless transactions through smart contracts and decentralized protocols. Users can engage in peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and increasing efficiency.
- Community Governance: Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) empower communities to participate in governance and decision-making processes. This fosters transparency, inclusivity, and decentralization of power within the network.
- Interoperability: Web3 promotes interoperability between different blockchain networks and decentralized applications (dApps). This facilitates seamless data exchange, interoperable assets, and enhances collaboration across the decentralized ecosystem.
Cons of Web2:
- Centralized Control: Web2 platforms are controlled by centralized entities, such as corporations or governments, leading to concerns over data monopolization, censorship, and lack of transparency.
- Data Exploitation: In Web2, user data is often harvested, monetized, and exploited by centralized platforms for targeted advertising and other purposes. This raises privacy concerns and undermines user autonomy.
- Single Point of Failure: Centralized Web2 platforms are susceptible to single points of failure, such as server outages or cyberattacks, which can disrupt services and compromise user data security.
- Lack of Transparency: Web2 platforms often lack transparency in their algorithms, content moderation policies, and decision-making processes, leading to concerns over bias, censorship, and manipulation of information.
- Limited User Control: Users have limited control over their data and digital identities in Web2, as centralized platforms dictate terms of service and privacy policies. This can result in user lock-in and difficulty in migrating data between platforms.
In summary, Web3 offers a decentralized, transparent, and user-centric alternative to centralized Web2 platforms, addressing key limitations such as data exploitation, lack of transparency, and centralized control. By leveraging blockchain technology, decentralized protocols, and community governance mechanisms, Web3 promotes trust, privacy, and empowerment for users in the digital age.
Conclusion
Building a decentralized social community on Web3 requires careful planning, technical expertise, and community engagement. By leveraging blockchain technology, implementing DAOs, and designing strategic roadmaps, businesses can create social networks that prioritize user ownership, privacy, and community governance. Embrace the principles of decentralization and empower users to take control of their digital experiences in the new era of Web3.